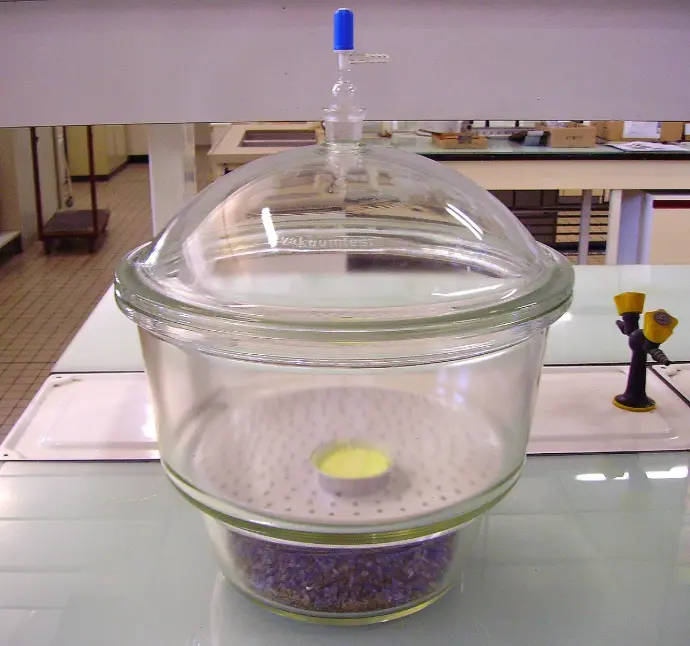
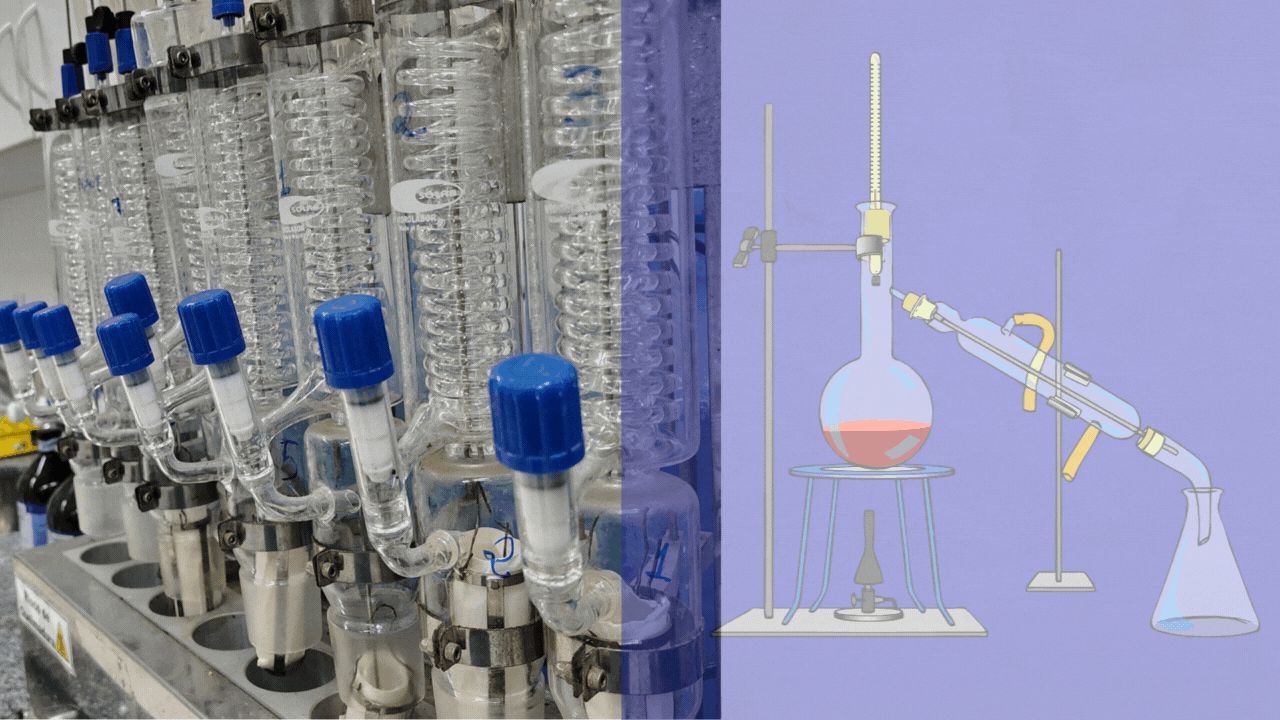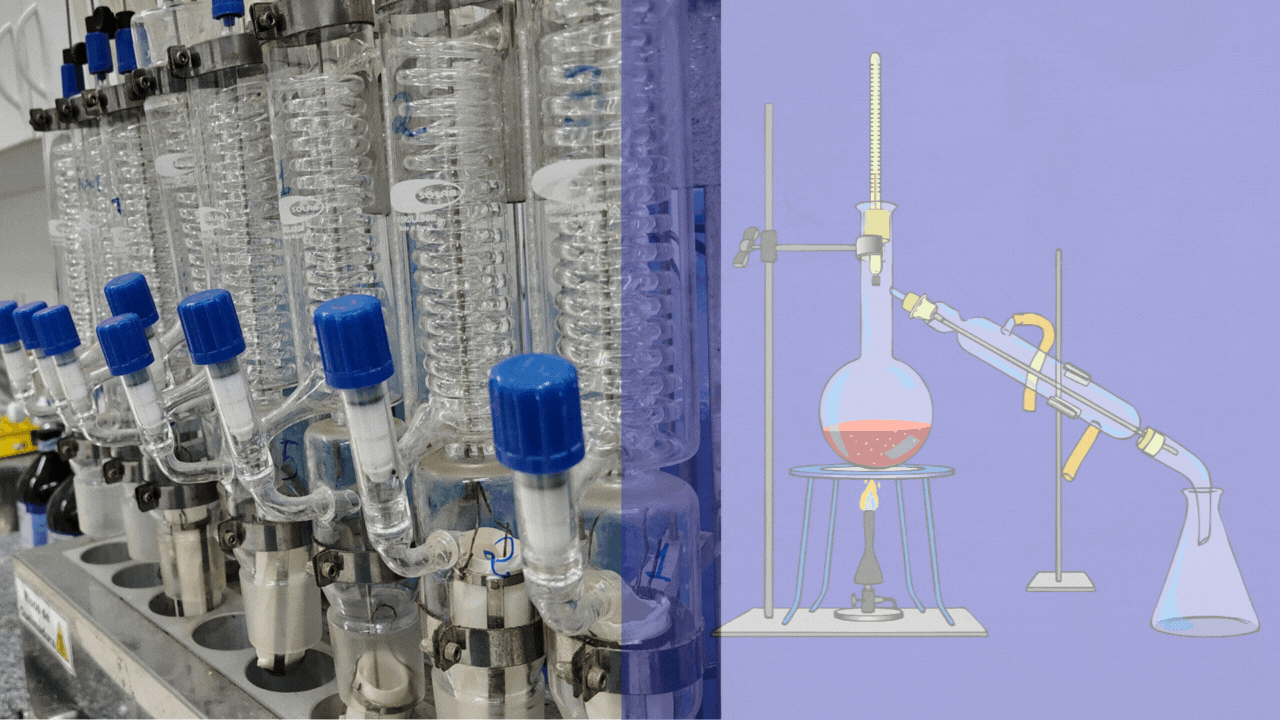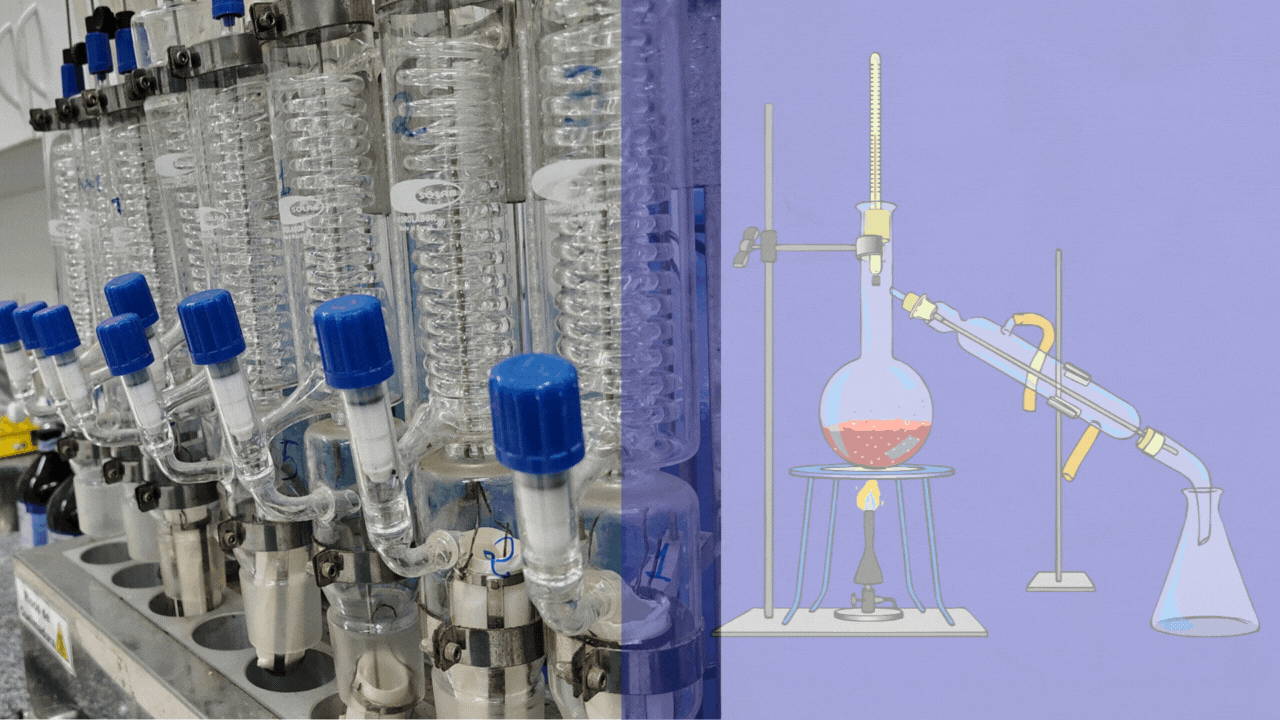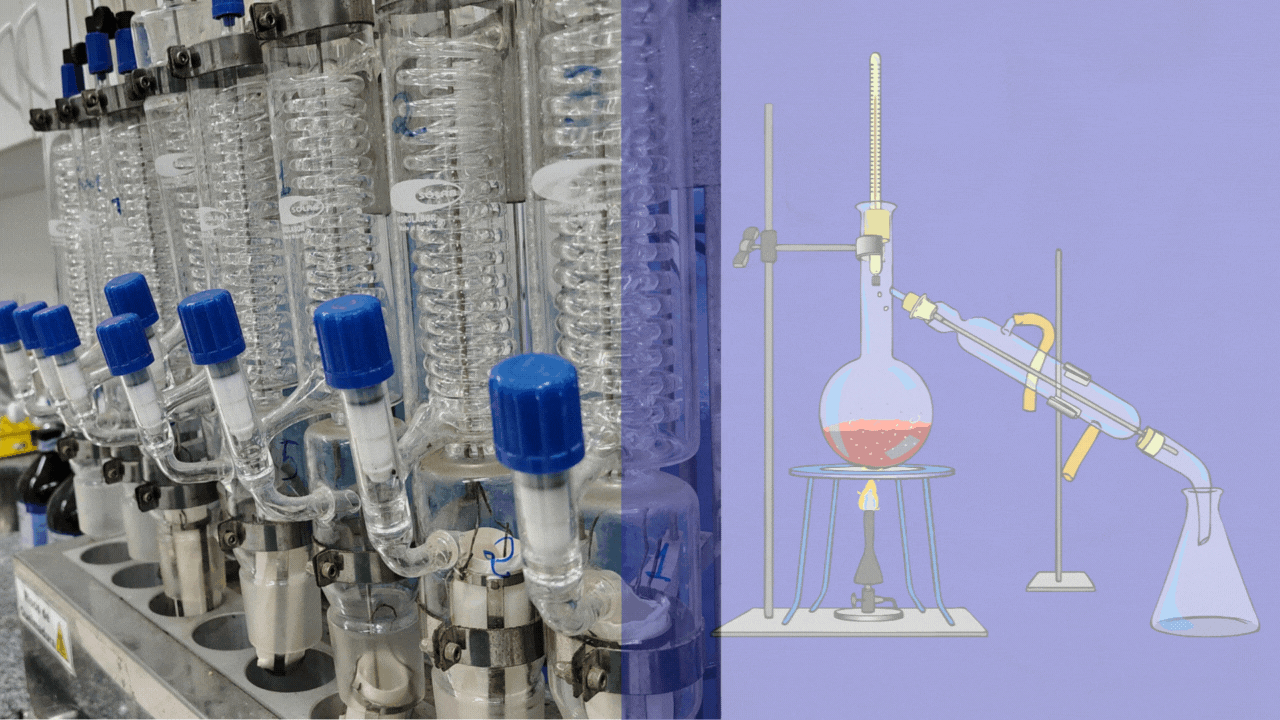
Welcome to the World of Laboratory Glassware
Glassware is the silent partner of every scientist. Behind every breakthrough in chemistry, biology, medicine, or physics, there are carefully designed pieces of laboratory glassware ensuring precision, safety, and reliability. From the humble beaker to advanced distillation systems, glassware transforms ideas into experiments and experiments into results.
A Journey Through History
Established as a distributor of laboratory glassware.
Expanded into scientific glassblowing and distillation technology after acquiring a specialized company in Los Angeles.
1980s: Entered the quartz glassblowing industry to meet the needs of the semiconductor market and later integrated chemical engineering expertise to develop waste recycling solutions.
Launched a spin-off dedicated to gas saturators and environmental solutions for wafer fabrication.
What Is Laboratory Glassware?

Laboratory glassware refers to a wide range of specially designed glass equipment used in scientific laboratories for performing experiments, preparing and storing solutions, analyzing substances, and observing chemical or biological reactions.
It is typically manufactured from borosilicate glass (such as Pyrex) or quartz, materials chosen for their resistance to heat, chemical corrosion, and mechanical stress. Laboratory glassware comes in standardized shapes and volumes to ensure accuracy, reproducibility, and safety in scientific work.
Discover more
The Importance of Laboratory Glassware
In the scientific world, laboratory glassware is far more than a collection of tools — it represents the backbone of reliable experimentation and discovery. Each piece is carefully designed to ensure that scientists, researchers, and students can obtain accurate, reproducible, and safe results across disciplines ranging from chemistry and biology to medicine, physics, and environmental science.

Safety and Durability
Made from high-quality materials like borosilicate (Pyrex) or quartz, glassware can withstand high temperatures, chemical corrosion, and repeated use.

Transparency and Observability
Clear glass allows scientists to observe reactions directly, ensuring control and safety during experiments.

Accuracy and Precision
Glassware ensures exact measurements of liquids and chemicals, which is critical for reliable results.

Versatility Across Disciplines
Laboratory glassware comes in countless shapes and sizes, each designed for a specific purpose, making it indispensable across all scientific fields.
Different Types of Laboratory Glassware and Their Uses

10. Specialized Quartz & Pyrex Glassware
Purpose: Quartz and borosilicate (Pyrex) glassware are designed for demanding experimental conditions, including high temperatures, UV exposure, and harsh chemicals. Quartz can withstand extremely high temperatures and transmit UV light, while Pyrex is resistant to thermal shock and corrosion.
Scientific Importance: These materials expand the frontiers of science by allowing experiments under conditions where normal glass would fail. They ensure durability, safety, and accuracy in cutting-edge research.
Applications:
- Quartz cuvettes for UV–Vis spectrophotometry in molecular biology and chemistry.
- Pyrex flasks and beakers for high-temperature reactions in teaching and research labs.
- Semiconductor industry, where quartz components are used in wafer fabrication.
- Advanced physics and photonics experiments requiring UV transparency.
Applications in Different Fields

Environmental Science:
Water and soil analysis, pollution testing.
Industry
Semiconductor production, food and beverage quality control, chemical engineering.

Choosing the Right Material
The selection of glassware material should always be guided by the nature of the experiment:
- For high-temperature reactions → Quartz.
- For daily chemical analyses → Borosilicate.
- For general, low-risk tasks → Soda-lime glass.
In scientific research, the wrong choice of glassware material can lead to contaminated results, equipment failure, or safety hazards. Thus, material science plays a pivotal role in the effectiveness of laboratory experiments.
Caring for Laboratory Glassware
Proper care and maintenance are essential to preserve the precision, durability, and safety of laboratory glassware. Neglecting cleaning or storage can lead to contamination, measurement errors, or even accidents.
Here’s a detailed care guide:
Practice | Description | Why It’s Important |
Immediate Cleaning | Wash glassware immediately after use with appropriate cleaning agents (e.g., mild detergents, chromic acid for stubborn residues). | Prevents residue buildup, contamination, and chemical reactions with leftover substances. |
Proper Rinsing | Always rinse with distilled or deionized water after cleaning | Ensures no ions or impurities remain, which could alter experimental results. |
Avoid Thermal Shock | Do not expose glassware to sudden temperature changes. Allow hot glass to cool before immersing in cold water. | Prevents cracking, breakage, and loss of samples. |
Inspection Before Use | Regularly check for chips, scratches, or cracks. Damaged glassware should be discarded. | Defective glassware compromises accuracy and poses safety risks. |
Sterilization | For microbiological and medical glassware, sterilize using autoclaves or dry heat ovens. | Ensures aseptic conditions for cultures and prevents contamination. |
Proper Storage | Store in clean, dry cabinets or racks, away from corrosive vapors. Use cushioned racks for fragile items like burettes and pipettes. | Protects against dust, moisture, and accidental breakage. |
Handling with Care | Always use tongs, gloves, or holders for hot glassware. Handle volumetric flasks and pipettes with precision. | Prevents accidents, burns, and contamination from skin oils. |
Innovations in Laboratory Glassware
Modern science demands tools that evolve with technology. Laboratory glassware is no longer just passive equipment — it is adapting to meet the needs of automation, sustainability, and digital integration.
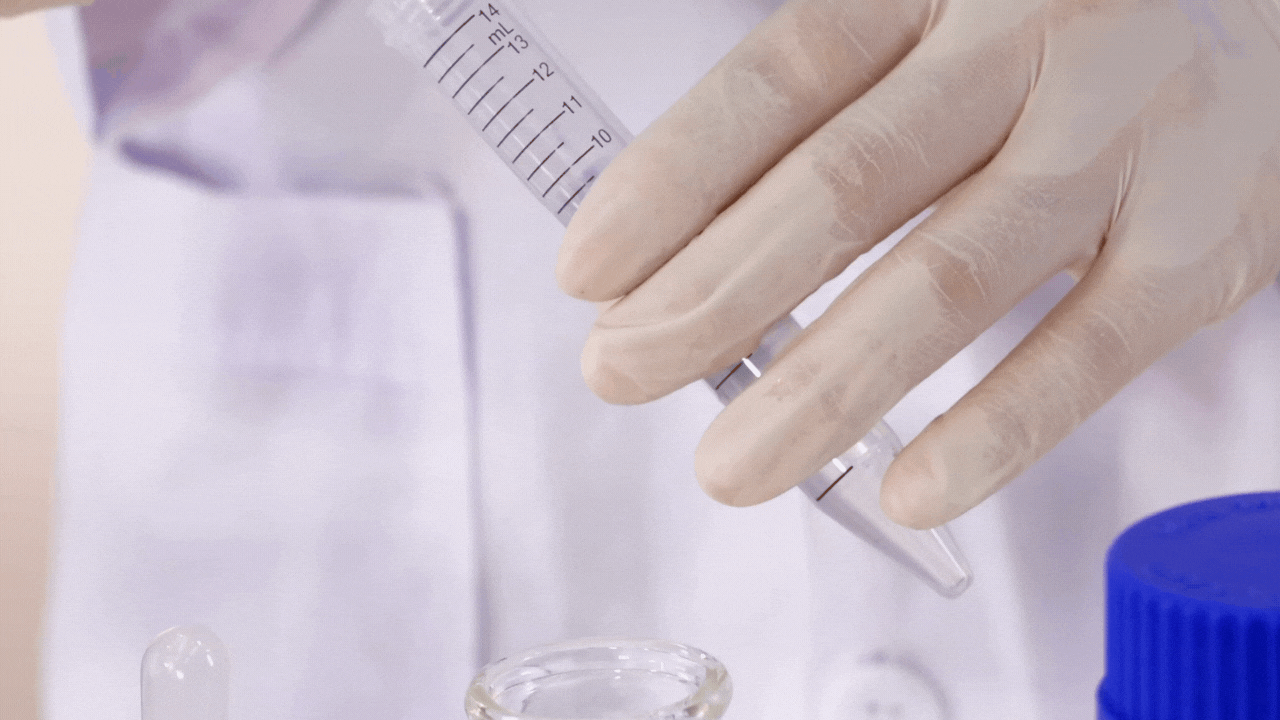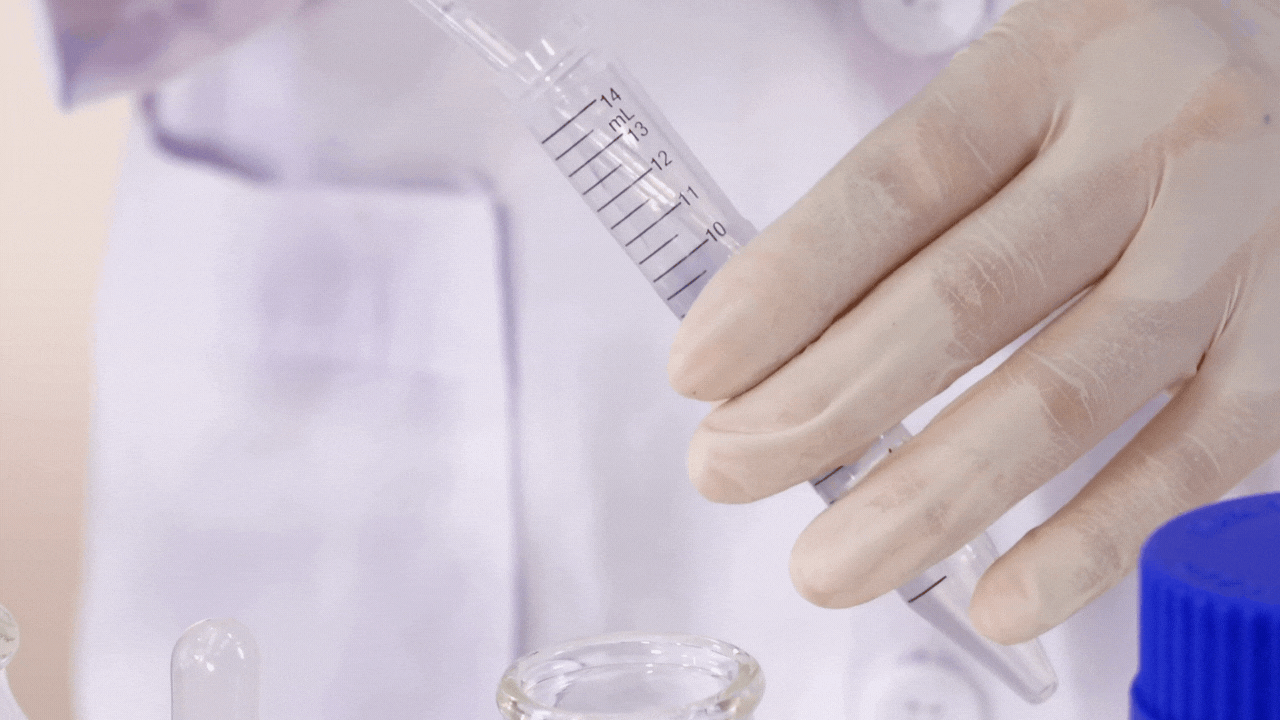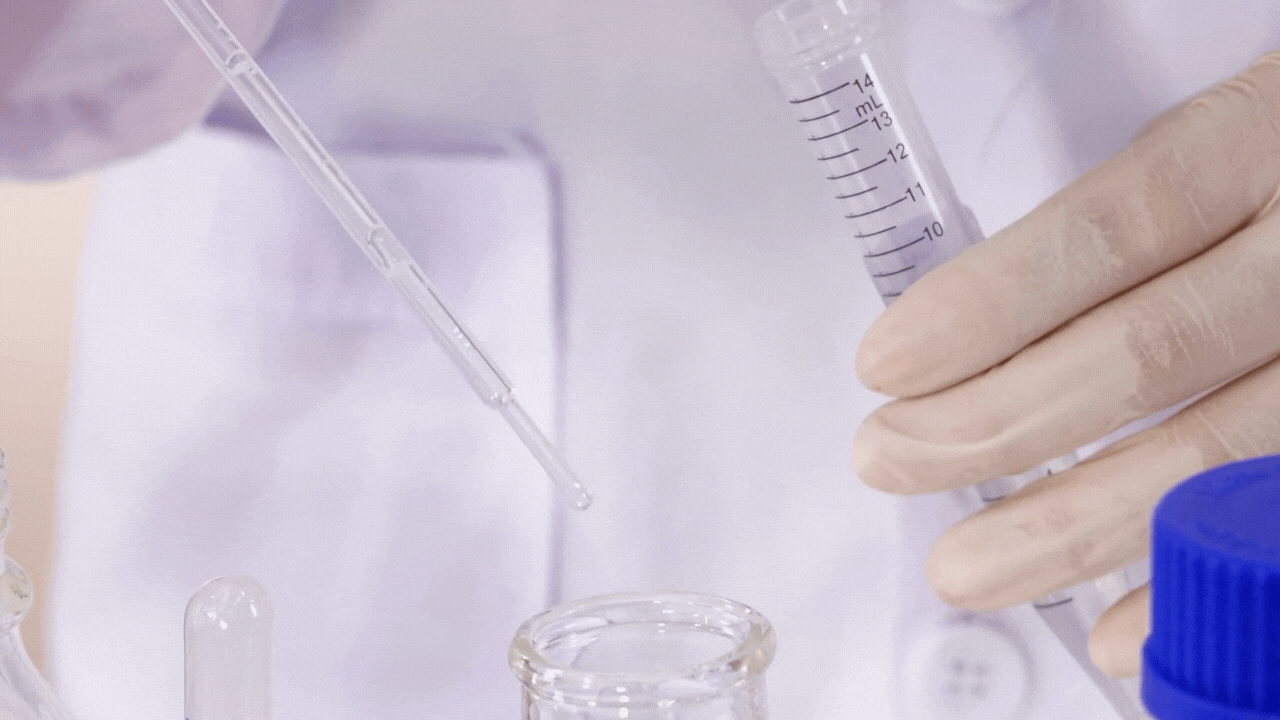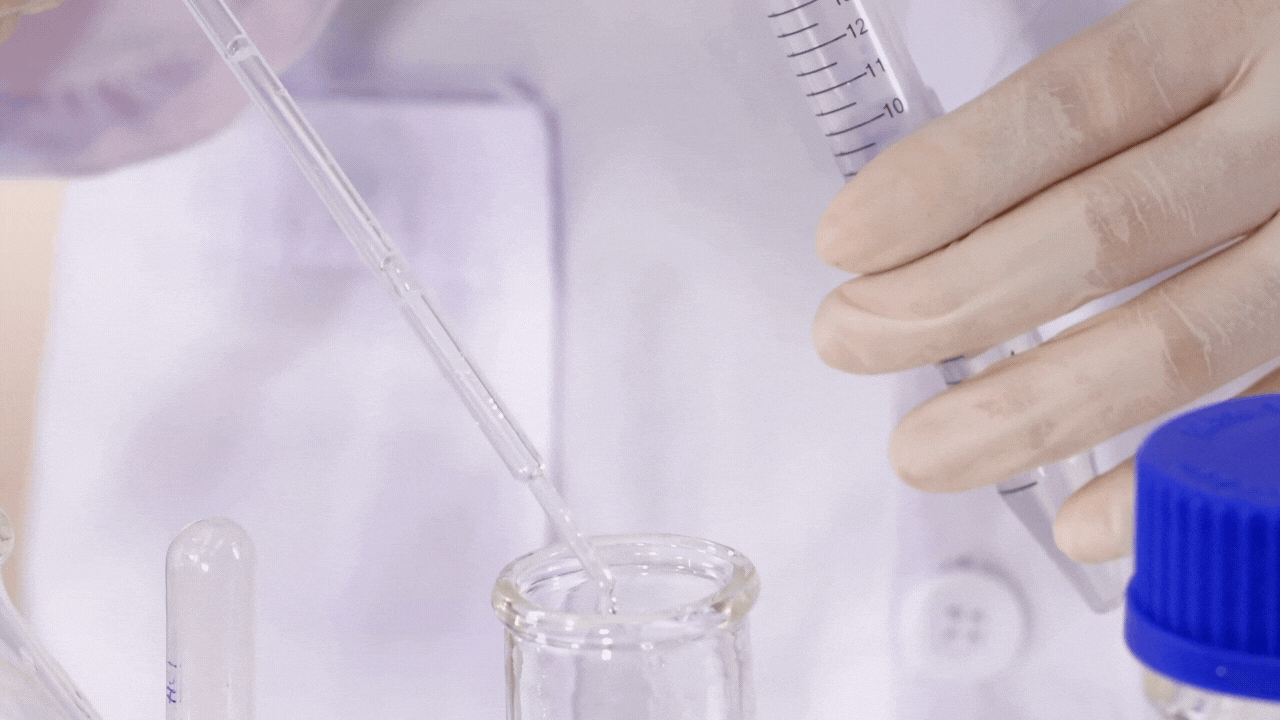
Smart Glassware
Integration of sensors, RFID chips, and data monitoring into beakers, flasks, and reactors allows real-time tracking of temperature, pH, or pressure.
Choosing the Right Glassware for Your Lab
Selecting laboratory glassware is a strategic decision. The wrong choice may lead to inaccurate results, unnecessary expenses, or safety hazards.
Key considerations:

Budget and Durability
Invest in Pyrex or quartz for long-term research, or soda-lime for routine, disposable tasks.
The Future of Laboratory Glassware
As science evolves, so too does laboratory glassware. The next generation of tools will combine sustainability, digitalization, and resilience:


Smart Glassware
Real-time monitoring of reactions with built-in sensors.

Eco-Stills and Green Distillation Systems:
Designed for sustainability, water recycling, and reduced environmental impact.

High-Strength Hybrid Materials:
Combining glass with ceramics or advanced composites to withstand harsher environments.

Full Automation:
Glassware integrated with robotic arms and AI-driven labs for faster, safer, and more reliable experiments.
Why Quality Matters
Accurate Data: Trusted results with minimal error.
Safe Experiments: Reduced risk of leaks, spills, or chemical accidents.
Durability: Longer lifespan under repeated heating, cooling, and chemical exposure.
Confidence in Outcomes: Reliable tools provide scientists with peace of mind.
The Language of Science
Laboratory glassware is more than just a set of tools it is the language through which scientists communicate with nature. Each flask, beaker, and pipette acts as a medium for discovery, innovation, and understanding.
Whether in a classroom experiment, a research laboratory, or a high-tech industrial facility, laboratory glassware remains the bridge between imagination and reality. It is the silent partner of every breakthrough, carrying humanity closer to uncovering the mysteries of the universe